时间:2024-07-12|浏览:232

用戶喜愛的交易所

已有账号登陆后会弹出下载
加密中的节点是什么?
加密节点是连接到区块链网络的计算机或服务器,在维护网络的完整性、安全性和功能性方面发挥着重要作用。节点存储、传播和保存区块链的数据,确保其连续性和账本的去中心化性质。下面,我将仔细研究加密中的节点是什么、它们的主要功能、节点类型以及如何设置自己的加密节点。
加密节点:摘要
加密节点是连接到区块链网络的重要计算机或服务器,对于维护网络的功能、安全性和完整性至关重要。
节点存储、传播和保存区块链数据,确保账本的连续性,促进区块链的去中心化特性,从而消除与中心控制相关的风险。
节点在区块链网络内以点对点方式运行,确保所有数据(如交易和新挖掘的区块)在区块链的所有副本中准确且一致地更新。
节点执行关键功能,例如通过加密检查验证新交易并遵循共识机制以就区块链的当前状态达成一致,确保统一性并防止欺诈。
常见的节点类型包括全节点、轻节点、挖掘节点、存档节点和验证器节点,每个节点都通过验证、存储或处理区块链交易在增强和保护区块链网络方面发挥着独特的作用。
什么是加密节点?
加密节点是指连接到区块链网络的计算机或服务器,在维护网络的功能、安全性和完整性方面起着至关重要的作用。这些节点存储、传播和保存区块链数据,从而确保账本的连续性和去中心化性质。
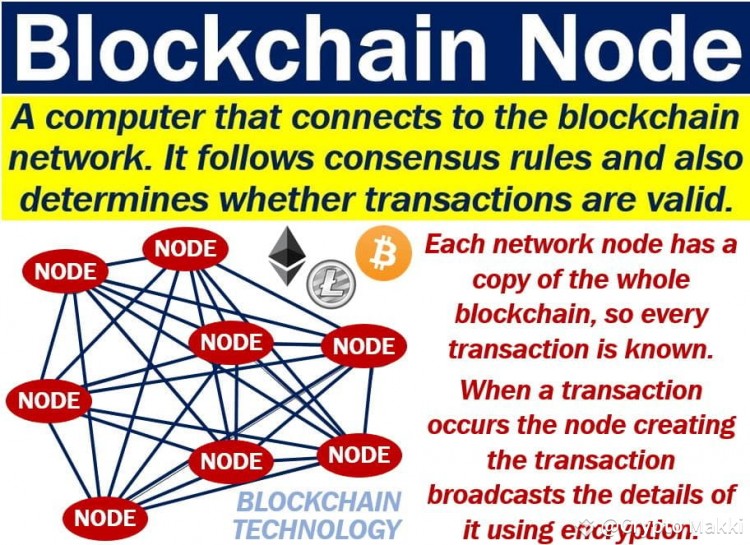
在区块链网络中,节点是各种技术和应用程序安全透明运行的基础。网络上的每个节点都保存整个区块链或其重要部分的副本,并与其他节点协同工作以维护账本的一致状态。通过节点,区块链实现了其去中心化的特性,因为它们遍布全球并由不同的个人或组织运营,从而消除了中央控制或单点故障的风险。
加密节点如何工作?
加密节点在对等网络上运行,构成区块链网络的主干。每个节点都与其他节点通信以传输交易数据和新挖掘的区块等信息,确保区块链在所有副本中的准确性和最新状态。以下是不同类型的节点对网络的贡献:
Consensus Mechanism: Nodes follow a consensus mechanism, a set of rules and processes through which all the nodes agree on the current state of the blockchain. This mechanism prevents fraud and ensures that each copy of the blockchain is identical across every node.
Transaction Validation: When a new transaction is made, it is broadcast to the network where nodes perform checks against previous transactions to confirm its validity using cryptographic techniques.
Block Propagation: Mining nodes, after successfully creating a new block, broadcast this block to the network. Full nodes then verify the block according to the blockchain’s rules and, upon validation, add it to their version of the blockchain.
Nodes are fundamental to the function and security of blockchain networks. They ensure the decentralization of the network, where no single entity has control over the entire blockchain. Here are the primary reasons why nodes are indispensable:
Decentralization: By hosting and updating copies of the blockchain independently, nodes ensure that the network remains decentralized, removing any single point of failure and making the system more resilient against attacks.
Security: Nodes help secure the blockchain by constantly verifying the blocks and transactions according to the consensus rules. This collective verification prevents the double-spending problem and ensures that no invalid transactions are recorded on the blockchain.
Transparency and Trust: Every transaction on the blockchain is verified by multiple nodes, which ensures its correctness and immutability. This process builds trust among users and enhances transparency, as every action taken on the network is publicly verifiable.
To summarize, crypto nodes are essential for the operation, security, and integrity of blockchain networks. By participating in the consensus mechanism and validating new transactions and blocks, nodes help maintain the blockchain as a trustworthy and decentralized ledger. Light nodes, mining nodes, and full nodes each play specific roles that ensure the blockchain remains efficient and scalable while requiring varying degrees of storage space and computational power.
Each type of node plays a unique role in enhancing and securing blockchain networks, ensuring their smooth operation and the integrity of the blockchain data. Whether through validating, storing, or processing blockchain transactions, these nodes collectively maintain the decentralized and distributed nature of blockchain technology.
Here are some of the major types of blockchain nodes used by various cryptocurrencies.
Full Nodesare the most robust type of nodes in blockchain networks: they maintain a complete and up-to-date copy of the entire blockchain ledger. These nodes independently verify all transactions and blocks against the blockchain’s rules, a process crucial for securing the network and preventing fraud. Full nodes play a vital role in the consensus process, as their comprehensive verification of the blockchain ensures that only valid transactions are confirmed and added to the blockchain. Operating a full node requires significant storage space and bandwidth, as it involves processing large amounts of data to keep the blockchain accurate and consistent.
Light Nodes, also known as SPV (Simplified Payment Verification) or lightweight nodes, require less storage space than full nodes, making them ideal for personal computers and mobile devices. Light nodes do not store the entire blockchain. Instead, they download only the block headers—small chunks of data that contain a summary of each block. This allows light nodes to verify the authenticity of transactions without complete information contained in full blocks. By querying full nodes (that do store the entire ledger) for specific transaction data, light nodes can confirm transaction validity efficiently and participate in the network with minimal resource usage.
Mining Nodesare specialized nodes that create new blocks in the blockchain through the process known as mining. Mining involves solving complex cryptographic puzzles to discover a new block, which is then added to the blockchain. These nodes perform this crucial function by bundling unconfirmed transactions into a block and then attempting to generate an acceptable hash for the block that meets the network’s difficulty criteria. Mining nodes are critical for processing and confirming transactions, adding them to the blockchain, and generating new coins. Not all mining nodes necessarily maintain a full copy of the blockchain, but they must engage in intensive computational operations to support the network.
Archival Nodesserve as historical record-keepers for blockchain networks. Unlike full nodes, which only need to keep the most recent states of the blockchain to verify transactions, archival nodes store the entire history of the blockchain transactions without pruning any data. This type of node is crucial for network participants who need access to the entire blockchain history for purposes such as complex data analysis, auditing, or the restoration of a node’s state. Archival nodes require significant storage capacity as they accumulate more data over time.
Validator Nodesare a key component in blockchain networks that use a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. These nodes are responsible for validating transactions and blocks, ensuring they adhere to the network rules. Validator nodes are selected based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. In return for their services and the risks they take (including the potential for penalties if they approve fraudulent transactions), validator nodes receive transaction fees and block rewards. Their role is pivotal in maintaining the network’s security and integrity without the high energy consumption associated with mining nodes.
Authority Nodesare specialized nodes found primarily in private or consortium blockchain networks. They maintain a comprehensive and authoritative copy of the blockchain ledger and have the exclusive right to validate and approve transactions. These nodes are typically operated by selected organizations or entities that have been granted special privileges due to their significant stake or trust within the network.
The crypto node setup process can vary slightly depending on whether one is setting up a full node, light node, or joining mining pools. Here’s a general guide to help you set up and run crypto nodes.









